- In Routing and Wavelength Assignment (RWA) problem,
in the absence of wavelength converters,
the task is to find such a route and a wavelength for each end-to-end lightpath
so that no link has two lightpaths sharing the same wavelength.
- In dynamic RWA problems, lightpath requests arrive according to (Poisson) process
- Currently established lightpaths correspond to the state of the system
- Decision on how customer/request is handled triggers a state change in the system
- Constitutes a MDP, where the objective is to minimize the blocking probability
- Enormous state space defies the computation of value functions, and thus also the policy iteration
- First policy iteration can be carried out by estimating the relative values by on-the-fly simulations [1-3]
Related publications:
| [1] |
E. Hyytiä and J. Virtamo,
Dynamic Routing and Wavelength Assignment Using First Policy Iteration,
in the Fifth IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, ISCC'2000,
pp. 146-151, 2000, Antibes, Juan les Pins, France.

|
| [2] |
E. Hyytiä and J. Virtamo,
Dynamic Routing and Wavelength Assignment Using First Policy Iteration, Inhomogeneous Traffic Case,
in the International Conference on Performance and QoS of Next Generation Networking, P&QNet2000, pp. 301-316, 2000, Nagoya, Japan.

|
| [3] |
E. Hyytiä and J. Virtamo,
Adaptive Importance Sampling in Routing and Wavelength Assignment,
European Transactions on Telecommunications (ETT), vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 331-339, 2002, Special Issue on Rare Event Simulation.

|
|
|
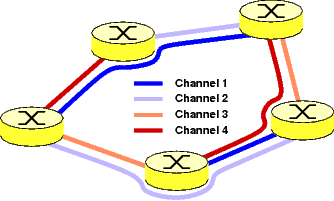 Figure: A sample RWA problem with 8 lightpaths.
Figure: A sample RWA problem with 8 lightpaths.
References:
- Richard Bellman, Dynamic programming, Princeton University Press, 1957.
- Sheldon M. Ross, Applied Probability Models with Optimization Applications,
Holden-Day Inc., 1970.
- Ronald A. Howard, Dynamic Probabilistic Systems, Volume II:
Semi-Markov and Decision Processes, Wiley Interscience, 1971.
|


